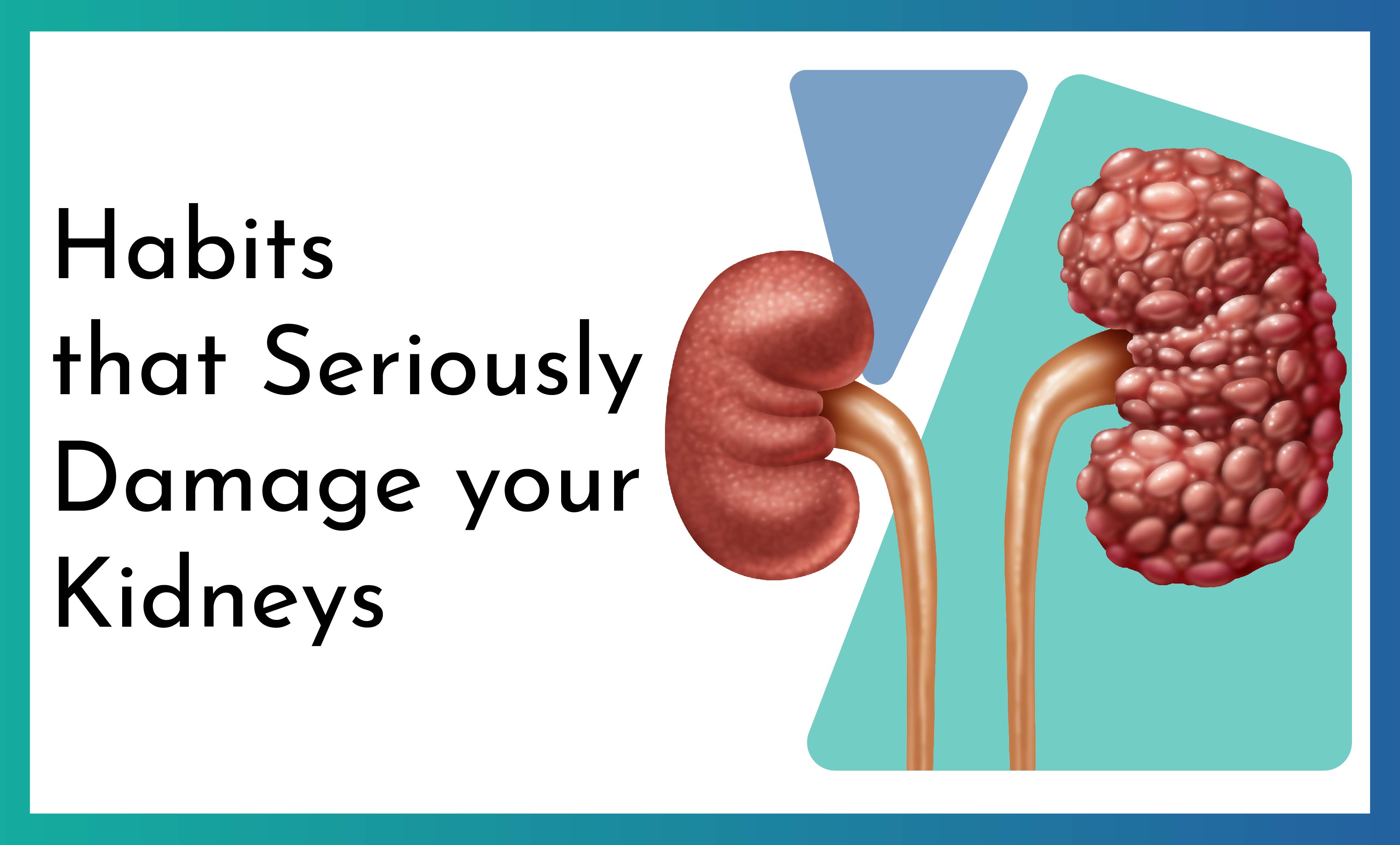
Habits that Seriously Damage your Kidneys
The kidneys are vital organ responsible for filtering waste products, balancing fluids, regulating electrolytes, and maintain overall health. Unfortunately, many common habits can damage these crucial organs over time.
- Overuse of
Painkillers:
Painkillers, especially non- steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) like
ibuprofen and
aspirin, are commonly used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. However, regular
use of
these medications can lead to kidney damage. NSAIDS reduce blood flow to kidneys,
impairing
their function. Over time, this can lead to chronic kidney disease or even acute
kidney failure.
Tips:
- Use NSAIDS sparingly and only when necessary.
- Opt for alternative pain relief method such as physical therapy,
acupuncture, or over-
the-counter acetaminophen (under a doctor’s guidance).
- Consult your doctor before taking any medications, especially if you have a
history of
kidney problems.
- Excessive salt
intake:
A diet high in salt can cause hypertension (high blood pressure), a major risk
factor for kidney
disease. Excessive sodium in the bloodstream forces the kidneys to work harder to
filter it out,
leading to long-term damage.
Tips:
- Limit your daily sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams (about one
teaspoon of salt).
- Avoid processed foods and read food labels to monitor sodium content.
- Season your meals with herbs and spices instead of salt.
- Insufficient Water
Intake:
Staying hydrated is crucial for kidney health. Dehydration reduces blood flow to the
kidneys,
leading to the accumulation of toxins and waste products. Over time, this can cause
kidney
stones and other complications.
Tips:
- Drink at least 8 glass of water a day
- Increase water intake if your active, live in a hot climate, or are ill
- Monitor your urine colour, pale yellow urine generally indicates proper
hydration.
- High Sugar
Consumption:
A diet high in sugar can lead to obesity and diabetes, both of which are major risk
factors for
kidney disease. Excess sugar can also cause high blood pressure, further increasing
risk.
Tips:
- Reduce your intake of sugar beverages, deserts, and snacks
- Opt for natural sweeteners like honey or stevia in moderation.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole
grains.
- Excessive alcohol
consumptions:
Alcohol can be toxic to the kidneys, especially when consumed in large amounts. It
causes
dehydration and increases blood pressure, which can strain the kidneys and lead to
long-term
damage.
Tips:
- Limit alcohol intake to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day
for men.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water alongside alcoholic beverages.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water alongside alcoholic beverages.
- Smoking:
Smoking is a major risk factor for kidney disease. It damages blood vessels,
reducing blood flow
to the kidneys and impairing their function. Smoking also increases the risk of high
blood
pressure and diabetes, both of which are harmful to the kidneys.
Tips:
- Seek support to quit smoking through counseling, nicotine replacement
therapies, or
prescription medications.
- Avoid exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet to
support smoking
cessation
- Overconsumption of
Red Meat:
High protein diets, particularly those rich in red meat, can put a strain on the
kidneys. The
process of metabolizing protein produces waste products that the kidneys must filter
out.
Excessive red meat consumption can lead to the formation of kidney stones and other
kidney-
related issues.
Tips:
- Limit red meat intake and incorporate plant-based protein sources such as
beans,
lentils, and tofu.
- Choose lean cuts of meat and opt for fish or poultry.
- Balance your diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Ignoring Kidney
Health Consumption:
Many people are unaware they have kidney issues because symptoms often do not appear
until
the condition is advanced. Ignoring early signs of kidney problems, such as changes
in urination,
swelling, or fatigue, can lead to severe kidney damage.
Tips:
- Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor to monitor kidney function.
- Be aware of your family history of kidney disease.
- Report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider promptly.
- Inadequate
Sleep:
Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to various health issues, including kidney
disease. Sleep is
essential for the body to repair itself, and lack of sleep can affect the
kidneys' ability to function
properly.
Tips:
- Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Avoid caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime.
- Misuse of
Supplements and Herbal Remedies:
While supplements and herbal remedies can offer health benefits, misuse or overuse
can harm
the kidneys. Some supplements contain high levels of minerals or toxins that can
accumulate in
the k
idneys and cause damage.
Tips:
- Consult your doctor before taking any supplements or herbal remedies.
- Follow recommended dosages and avoid combining multiple supplements without
medical advice
- Choose supplements from reputable sources to ensure quality and safety.
- Holding in
Urine:
Regularly delaying urination can cause bladder and kidney problems. Holding in urine
increases
pressure in the urinary tract, leading to infections and potentially damaging the
kidneys.
Tips:
- Urinate as soon as you feel the urge.
- Stay hydrated to maintain regular urination patterns.
- Practice good hygiene to prevent urinary tract infections.
- Ignoring Diabetes
and Hypertension Management:
Diabetes and hypertension are the leading causes of kidney disease. Poor management
of these
conditions can accelerate kidney damage and lead to kidney failure.
Tips:
- Follow your doctor's recommendations for managing diabetes and
hypertension.
- Monitor your blood sugar and blood pressure regularly.
- Maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and take prescribed
medications as directed.
- High Phosphorous
Intake:
Foods high in phosphorus, such as processed foods and carbonated drinks, can be
harmful to
the kidneys. Excessive phosphorus can cause calcification in the kidneys, leading to
damage over
time.
Tips:
- Limit consumption of processed foods and sodas.
- Choose fresh, whole foods over packaged and processed options.
- Consult your doctor or a dietitian to monitor phosphorus levels if you have
kidney
concerns.
- Prolonged Use of
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs):
PPIs, commonly used to treat acid reflux and heartburn, can increase the risk of
chronic kidney
disease if used long-term. These medications can affect kidney function and lead to
kidney
damage.
Tips:
- Use PPIs only as directed by your doctor.
- Explore alternative treatments for acid reflux, such as dietary changes and
natural
remedies.
- Regularly review your medications with your healthcare provider.
Painkillers, especially non- steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) like ibuprofen and aspirin, are commonly used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. However, regular use of these medications can lead to kidney damage. NSAIDS reduce blood flow to kidneys, impairing their function. Over time, this can lead to chronic kidney disease or even acute kidney failure.
Tips:
- Use NSAIDS sparingly and only when necessary.
- Opt for alternative pain relief method such as physical therapy, acupuncture, or over- the-counter acetaminophen (under a doctor’s guidance).
- Consult your doctor before taking any medications, especially if you have a history of kidney problems.
A diet high in salt can cause hypertension (high blood pressure), a major risk factor for kidney disease. Excessive sodium in the bloodstream forces the kidneys to work harder to filter it out, leading to long-term damage.
Tips:
- Limit your daily sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams (about one teaspoon of salt).
- Avoid processed foods and read food labels to monitor sodium content.
- Season your meals with herbs and spices instead of salt.
Staying hydrated is crucial for kidney health. Dehydration reduces blood flow to the kidneys, leading to the accumulation of toxins and waste products. Over time, this can cause kidney stones and other complications.
Tips:
- Drink at least 8 glass of water a day
- Increase water intake if your active, live in a hot climate, or are ill
- Monitor your urine colour, pale yellow urine generally indicates proper hydration.
A diet high in sugar can lead to obesity and diabetes, both of which are major risk factors for kidney disease. Excess sugar can also cause high blood pressure, further increasing risk.
Tips:
- Reduce your intake of sugar beverages, deserts, and snacks
- Opt for natural sweeteners like honey or stevia in moderation.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Alcohol can be toxic to the kidneys, especially when consumed in large amounts. It causes dehydration and increases blood pressure, which can strain the kidneys and lead to long-term damage.
Tips:
- Limit alcohol intake to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water alongside alcoholic beverages.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water alongside alcoholic beverages.
Smoking is a major risk factor for kidney disease. It damages blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the kidneys and impairing their function. Smoking also increases the risk of high blood pressure and diabetes, both of which are harmful to the kidneys.
Tips:
- Seek support to quit smoking through counseling, nicotine replacement therapies, or prescription medications.
- Avoid exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet to support smoking cessation
High protein diets, particularly those rich in red meat, can put a strain on the kidneys. The process of metabolizing protein produces waste products that the kidneys must filter out. Excessive red meat consumption can lead to the formation of kidney stones and other kidney- related issues.
Tips:
- Limit red meat intake and incorporate plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, and tofu.
- Choose lean cuts of meat and opt for fish or poultry.
- Balance your diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Many people are unaware they have kidney issues because symptoms often do not appear until the condition is advanced. Ignoring early signs of kidney problems, such as changes in urination, swelling, or fatigue, can lead to severe kidney damage.
Tips:
- Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor to monitor kidney function.
- Be aware of your family history of kidney disease.
- Report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider promptly.
Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to various health issues, including kidney disease. Sleep is essential for the body to repair itself, and lack of sleep can affect the kidneys' ability to function properly.
Tips:
- Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Avoid caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime.
While supplements and herbal remedies can offer health benefits, misuse or overuse can harm the kidneys. Some supplements contain high levels of minerals or toxins that can accumulate in the k idneys and cause damage.
Tips:
- Consult your doctor before taking any supplements or herbal remedies.
- Follow recommended dosages and avoid combining multiple supplements without medical advice
- Choose supplements from reputable sources to ensure quality and safety.
Regularly delaying urination can cause bladder and kidney problems. Holding in urine increases pressure in the urinary tract, leading to infections and potentially damaging the kidneys.
Tips:
- Urinate as soon as you feel the urge.
- Stay hydrated to maintain regular urination patterns.
- Practice good hygiene to prevent urinary tract infections.
Diabetes and hypertension are the leading causes of kidney disease. Poor management of these conditions can accelerate kidney damage and lead to kidney failure.
Tips:
- Follow your doctor's recommendations for managing diabetes and hypertension.
- Monitor your blood sugar and blood pressure regularly.
- Maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and take prescribed medications as directed.
Foods high in phosphorus, such as processed foods and carbonated drinks, can be harmful to the kidneys. Excessive phosphorus can cause calcification in the kidneys, leading to damage over time.
Tips:
- Limit consumption of processed foods and sodas.
- Choose fresh, whole foods over packaged and processed options.
- Consult your doctor or a dietitian to monitor phosphorus levels if you have kidney concerns.
PPIs, commonly used to treat acid reflux and heartburn, can increase the risk of chronic kidney disease if used long-term. These medications can affect kidney function and lead to kidney damage.
Tips:
- Use PPIs only as directed by your doctor.
- Explore alternative treatments for acid reflux, such as dietary changes and natural remedies.
- Regularly review your medications with your healthcare provider.